Horizontally Scaling Realtime Applications
Introduction
It is no secret that any respectable software that's part of the SAAS revolution has to support realtime features. From a UX perspective, it's a huge win and one of the bare minimum expectations of a modern application.
Now, let's talk implementation. As a young developer, I was proud to make my share of "realtime" apps that used one of the below approaches:
- HTTP Polling
- Firebase
- Supabase
- Single host socket.io chat application
HTTP Polling is not perfect for usecases where lower latency is required.
Firebase and Supabase are Backend as a service tools that are popularly used by beginners as well as small developer teams. These provide an abstraction to subscribe to the entire Database changes. While this works for some scenarios, it may not be suitable for everything. Either ways, it's useful to understand the underlying infrastructure and work on our system design knowledge.
"How to make a websocket chat application using socket.io" is a very common and cool tutorial. It gave me my first dip into working with and understanding the WebSocket protocol. In this article, we will explore and build on top of this set up. Explore how well it scales.
The Project - Tic Tac Toe
Instead of the boring old chat application, for our demo, we will build an online multiplayer Tic Tac Toe application with the following goals:
- Horizontally scalable (Optimize throughput)
- Self Healing
We'll also go over different scenarios and theoretical concepts involved for the same.
You can find the code deployed and play it with friends 😄. The source code is available on GitHub.
This frontend is a simple React Application, the Backend is written using Node.js, Express, Prisma. Socket.io is used on both client and server side as a lightweight abstraction on top of the websocket protocol. RabbitMQ is used for Pub Sub.
Architecture Overview
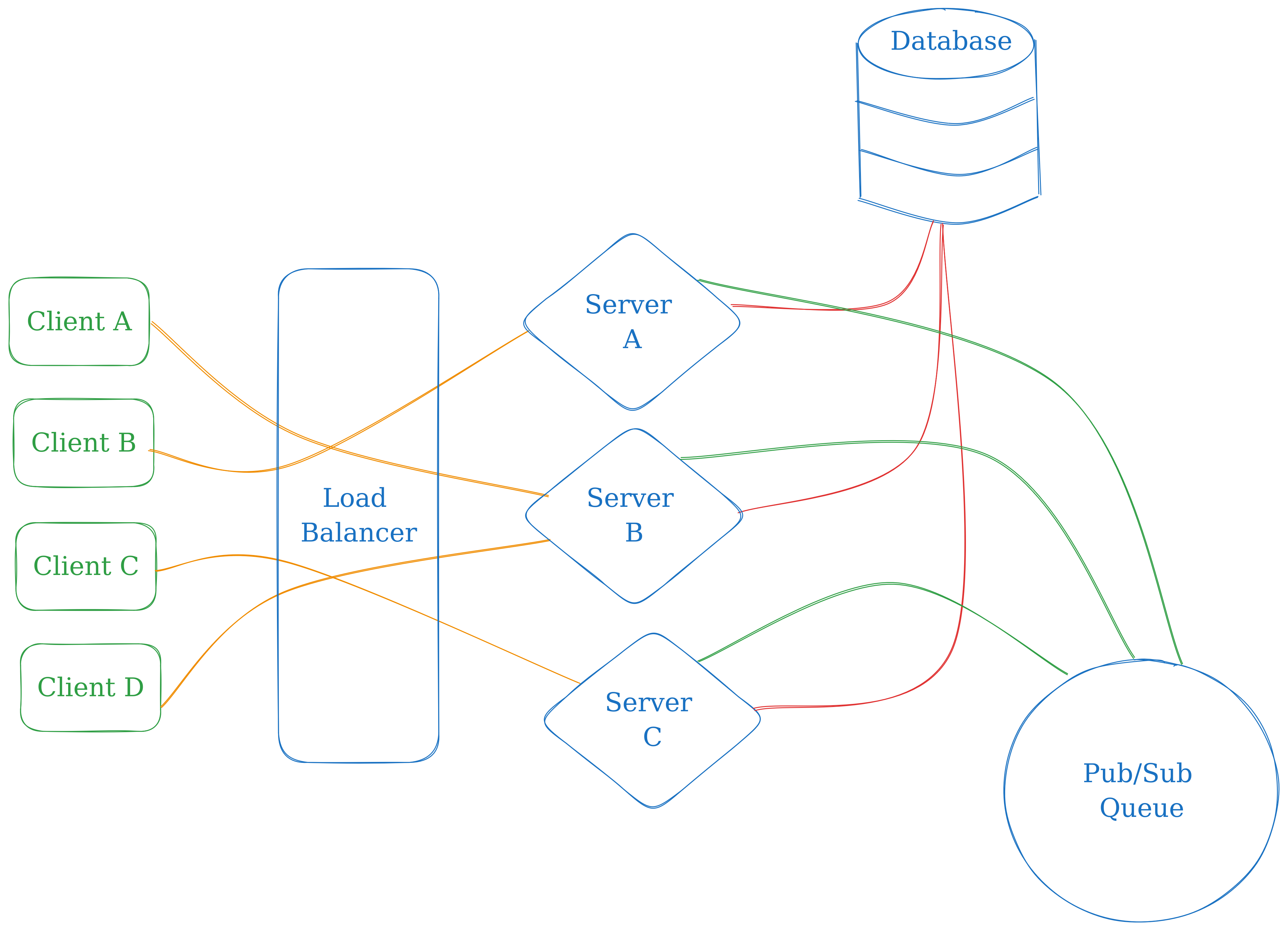
There is 4 different kind of components in use:
- Layer 4 Load Balancer
- Is aware of the health of server instances in real time.
- Does automatic reconfiguration of routing when a server instance goes down or goes back up.
- Can be horizontally scaled if required.
- Server instances
- Handles creating and assigning a new session.
- Handles business logic of Tic Tac Toe
- Publishes to "new-move" topic when a player makes a move.
- Listens to "new-move" topic and emits it back to client's socket connection
- Can be horizontally scaled by adding more instances and keeping the Load Balancer aware.
- Database
- Stores Session and Game State information
- Acts as a Fail Safe if the Queue/WebSocket system goes down.
- Reads can be Horizontally scaled using Read Replicas
- Writes may be scaled using Sharding if it fits the use case.
- Queue
- Configured in Pub/Sub architecture.
- Can be horizontally scaled by adding more nodes to the cluster.
Pub/Sub Architecture in real-time applications
In real-time applications, Pub/Sub is commonly used for distributing messages to multiple clients without direct coupling between producer and consumer. One key aspect to take away is that, producers, consumers, as well as the queue itself can be horizontally scaled and scaled separately.
Scaling dynamics of queues:
- More cores/nodes are utilized for tasks like processing, routing, and delivering messages. These facilitate more throughput in the system.
- More memory helps in higher retention of messages. As the number of topics or the message load increase, memory usage can grow substantially. Setting limits on message retention and leveraging disk storage for older messages can help prevent memory exhaustion.
Building Resilient Systems
- On the server side, if a client disconnects, it needs to cleanup/deregister its callback/subscription to listening to the pub/sub queue.
- If an unexpected disconnection happens on the client side (Example, server crashes), the client should try to automatically reconnect.
- This system is self-healing, and inspite of sticky sessions, scales well horizontally.
Architectural Considerations and strategies
- Distributed state may not be same at all places at any point of time (Eventual consistency). Your system needs to understand and adopt such that the key information is obtained and used correctly.
- Idempotency, baked into the system adds simplicity. It ensures that the same operation can be repeated multiple times without changing the result beyond the initial application. This is important in case of network failures.
- Example - I send the state of the entire game on each new move to both clients instead of just the move. This way, if a client misses a move, or has some glitch, it can catch up by just updating the state.
- Most pub/sub implementations designed in a way that I cannot have shortlived dynamic topics. I publish to a singular shared topic such as "new-move" then each service subscribed to it does its own filtering.
- It is worth noting that when we are trying to optimize for throughput, this "filtering" can be a bottleneck. It is important to understand the tradeoffs and optimize accordingly.